
- #FREE42 SIMULATOR HOW TO#
- #FREE42 SIMULATOR MANUAL#
- #FREE42 SIMULATOR FULL#
- #FREE42 SIMULATOR SIMULATOR#
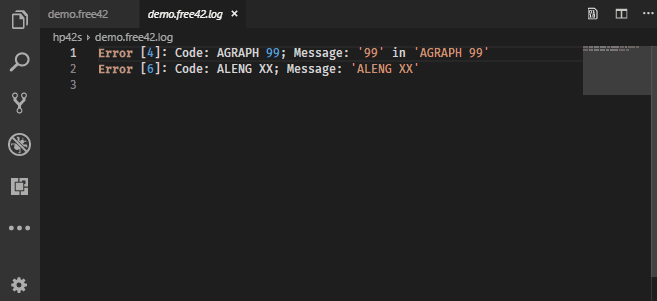
# yes, the multiplication between 1/3 and x^3 is missing. # a bit off, something went wrong, let's check the program again. # use PRINT PRUSR to see that the program is there. # and those have to be declared right after the label # we need to name variables with MVAR for the solver # now we can name the program, max 7 characters. # PRGM works also if by mistake one leaves the programming mode, typing it again # END is shown, we will not have to type it when typing whatever program

# the new program area is shown by a 0-byte program # this creates a new program area (programs areas are delimited by a starting label and and END # actually the solver allows constant in the integration, but this will be shown in another example # a bit more tedious than the 506w, but it will be good to introduce some basic programming. # we have to program a function to make a numerical integration # 2*pi cannot be entered, so it is saved first in a variable, like A, then recalled. # 1/3 typed as fraction of the type "a b/c" We integrate \( 1/3 \cdot x^3 \) between 5 and 12, then \( sin(x) \) between 0 and \( 2 \cdot \pi \) Numerical integration, basic programming needed on Free42
#FREE42 SIMULATOR HOW TO#
Surely there exist a listing providing them (TODO: find them and showing how to integrate them), but the point that are not built in. # sqrt(6) stored in A and then recalled when asked.Īt the moment numerical differentiation seems not available as built in function in f42. # 506w (typing 1/3 as fraction with the command "a b/c" ) We have \( f(x) = x^2 \) so \( f'(x) = 2x \), what about computing it in \( \sqrt \) and \( 8 \). If instead I clear X, Y is not affected because the stack # because if I type 63 5 + (= 68)and then last X without clearing X before # last X can be used to but in cooperation with drop of the register X # This is how the CLX function works (or clx). # because we just used the register X together with Y but Y is not consumed. # actually with this operation we never activate the stack drop,

#FREE42 SIMULATOR FULL#
Typing: 117 enter enter enter (check with Rdown that the stack is full of 117) In short, when numbers are entered they lift the stack, when they are “consumed” the stack drops replicating the last register, T. The f42 achieve this with how the stack registers ( X, Y, Z, T ) are designed. On the 506w there is the possibility to do constant calculation. Also the 506w commands can be read on the manual, so I would post non-obvious procedures only for the F42. If the reader does not know the RPN, nevertheless the examples here written (one should deduce the syntax thought) or the documentation provided by the Free42 homepage would be enough to master it. The HP 42s (or Free 42) uses the RPN notation that is assumed known by the reader. Indeed it is an exploration.ĭuring the comparison, some operations, assumed to be “common” would be skipped. Moreover the exploration may miss functions declared as “not there” but being implemented in the free42. Why scientific calculators? Because the HP 42s is advertised so, rather than being programmable. The same comparison can be made with other non-programmable non-graphing scientific calculators. It is like an exploration by comparison and of course it will miss functions that are partially mentioned or absent on the sharp 506w. From now on the Free42 is mentioned as f42 or and the sharp el 506w is mentioned as 506w.
#FREE42 SIMULATOR MANUAL#
This article is made as a byproduct of exploring the Free42 while trying to find out if the functions mentioned in the manual of the sharp el 506w (produced in the early 2000, the manual was made for 506w and 546w models), a scientific calculator not programmable and not graphing, are present on the HP 42s or better on the Free42.
#FREE42 SIMULATOR SIMULATOR#
Free42 is a simulator (not an emulator) of the HP 42s, and it is a neat work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
